I recently came across an open-source tool called PDFMathTranslate. It can translate PDF files into multiple languages without breaking the layout.

Curious about how it handles PDF parsing under the hood, I decided to dig into the source code.
In this article, first, I’ll walk through the code, then share a few thoughts and reflections.
Overview
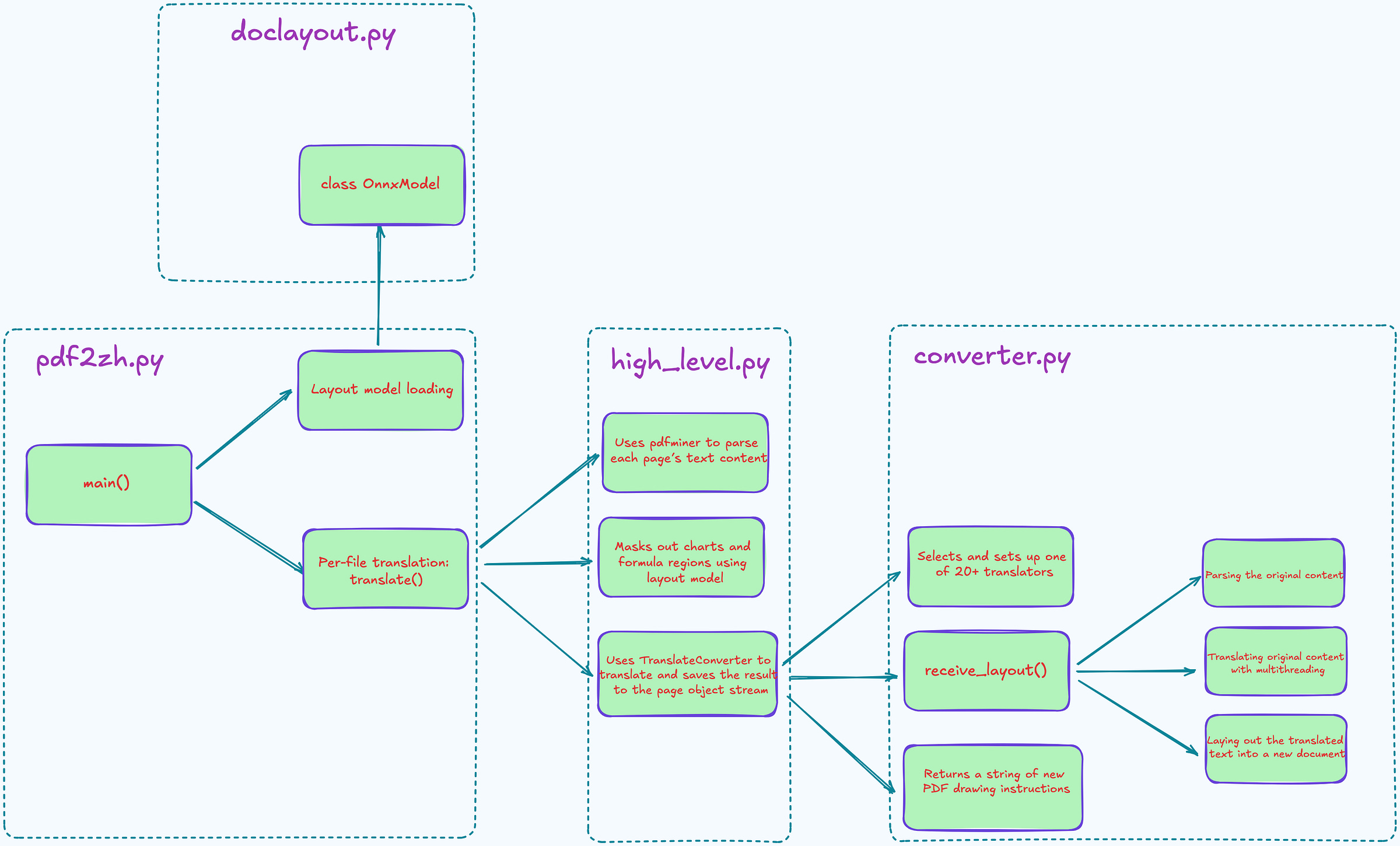
Since the project doesn’t include an architecture diagram, so I sketched one myself while exploring the code—just to focus on the PDF parsing logic.
Main Entry
The core functionality of PDFMathTranslate lives in the pdf2zh directory, with pdf2zh.py serving as the main entry point.
pdf2zh.py is a command-line tool that extracts both text and images from the original file, runs the text through your chosen translation service (Google, OpenAI, and over 20 others), and then generates a translated PDF. It also supports multiple runtime modes, including GUI, web interface, and Celery-based task queues.
def main(args: Optional[List[str]] = None) -> int:
from rich.logging import RichHandler
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO, handlers=[RichHandler()])
# disable httpx, openai, httpcore, http11 logs
logging.getLogger("httpx").setLevel("CRITICAL")
logging.getLogger("httpx").propagate = False
logging.getLogger("openai").setLevel("CRITICAL")
logging.getLogger("openai").propagate = False
logging.getLogger("httpcore").setLevel("CRITICAL")
logging.getLogger("httpcore").propagate = False
logging.getLogger("http11").setLevel("CRITICAL")
logging.getLogger("http11").propagate = False
parsed_args = parse_args(args)
if parsed_args.config:
ConfigManager.custome_config(parsed_args.config)
if parsed_args.debug:
log.setLevel(logging.DEBUG)
if parsed_args.onnx:
ModelInstance.value = OnnxModel(parsed_args.onnx)
else:
ModelInstance.value = OnnxModel.load_available()
if parsed_args.interactive:
from pdf2zh.gui import setup_gui
if parsed_args.serverport:
setup_gui(
parsed_args.share, parsed_args.authorized, int(parsed_args.serverport)
)
else:
setup_gui(parsed_args.share, parsed_args.authorized)
return 0
if parsed_args.flask:
from pdf2zh.backend import flask_app
flask_app.run(port=11008)
return 0
if parsed_args.celery:
from pdf2zh.backend import celery_app
celery_app.start(argv=sys.argv[2:])
return 0
if parsed_args.prompt:
try:
with open(parsed_args.prompt, "r", encoding="utf-8") as file:
content = file.read()
parsed_args.prompt = Template(content)
except Exception:
raise ValueError("prompt error.")
print(parsed_args)
if parsed_args.babeldoc:
return yadt_main(parsed_args)
if parsed_args.dir:
untranlate_file = find_all_files_in_directory(parsed_args.files[0])
parsed_args.files = untranlate_file
translate(model=ModelInstance.value, **vars(parsed_args))
return 0
translate(model=ModelInstance.value, **vars(parsed_args))
return 0The main logic of pdf2zh.py centers around the main() function, with two key parts worth noting:
Layout model loading (
OnnxModel.load_available()or a custom model via--onnx): Uses an ONNX-based layout model (likeDocLayout-YOLO) to detect paragraph, formula, and image regions—laying the groundwork for aligned translation later on.Per-file translation (translate()): Handles everything from parsing the original PDF, running the translation, rebuilding the layout, and generating output PDF.
Translate
Next, let’s take a closer look at the translate() function, which lives in high_level.py. Think of high_level.py as the engine behind the entire PDF translation pipeline. For each PDF, it
Parses the layout and extracts text blocks and images
Calls the translation service concurrently (number of threads controlled by
--thread)Rebuilds the layout
Generate output PDFs
Keep reading with a 7-day free trial
Subscribe to AI Exploration Journey to keep reading this post and get 7 days of free access to the full post archives.